When it comes to fitness, the term best workout routine is as elusive as it is subjective. The ideal workout plan is deeply personal, influenced by factors such as your fitness goals, current level of fitness, time constraints, and even personal preferences. This blog will explore various types of workout routines, their benefits, and how to tailor a plan to meet your individual needs.

Understanding Your Fitness Goals
Before diving into specific routines, it is crucial to identify your fitness goals. Here are some common objectives and how they influence workout choices:
Weight Loss
If your primary goal is to shed pounds, your routine should include a mix of cardiovascular exercises and strength training. Cardio workouts like running, cycling, or swimming help burn calories, while strength training builds muscle, which increases your resting metabolic rate.
Muscle Gain
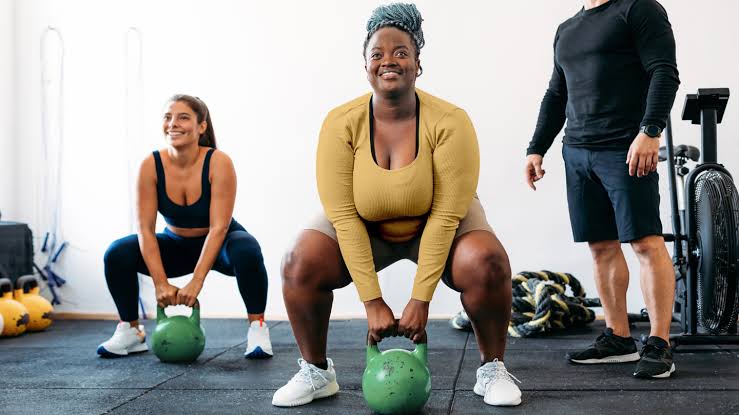
For those looking to build muscle, a strength training-focused routine is essential. This typically involves lifting heavier weights with lower repetitions and longer rest periods between sets to maximize muscle growth.
Improved Endurance
To enhance cardiovascular endurance, focus on activities that increase your heart rate for extended periods. Long-distance running, cycling, and rowing are excellent choices.
General Fitness
If you seek overall health and fitness, a balanced routine that incorporates cardio, strength training, and flexibility exercises is ideal. This well-rounded approach ensures you are working all aspects of physical fitness.
Flexibility and Mobility:
For improved flexibility and mobility, incorporate yoga or dynamic stretching into your routine. These practices enhance your range of motion and can prevent injuries.
Key Components of a Workout Routine
Cardiovascular Exercise
Cardiovascular workouts improve heart health and increase calorie burn. Options include running, cycling, swimming, and high-intensity interval training (HIIT). Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity cardio per week.
Strength Training
Strength training builds muscle, enhances bone density, and boosts metabolism. Incorporate exercises that target major muscle groups using weights, resistance bands, or bodyweight. Include exercises like squats, deadlifts, push-ups, and rows.
Flexibility and Mobility
Stretching and mobility exercises improve your range of motion and reduce the risk of injury. Incorporate dynamic stretches before workouts and static stretches after. Yoga and Pilates are excellent for increasing flexibility.
Balance and Stability
Exercises that challenge your balance and stability can enhance core strength and prevent falls. Incorporate balance exercises like single-leg stands or use stability balls and balance boards.
Types of Workout Routines
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) HIIT alternates between short bursts of intense exercise and periods of lower-intensity recovery. This approach maximizes calorie burn in a short period and can improve both cardiovascular and muscular fitness. A typical HIIT session might involve 30 seconds of sprinting followed by 30 seconds of walking, repeated for 20-30 minutes. Benefits: Efficient calorie burning Time-saving Enhances cardiovascular fitness Considerations: Intense and may not be suitable for beginners Requires adequate recovery time 2. Strength Training Strength training focuses on building muscle through resistance exercises. This can be achieved with free weights, machines, or bodyweight exercises. Typically, it involves performing 3-4 sets of 8-12 repetitions of various exercises targeting different muscle groups. Benefits: Increases muscle mass Boosts metabolism Improves bone density Considerations: Requires proper form to avoid injury Progress may be slow initially 3. Cardiovascular Training Cardio training includes exercises that elevate your heart rate. Activities like running, swimming, and cycling are excellent for improving heart health and endurance. Cardio can be performed in steady-state (e.g., jogging for 30 minutes) or interval (e.g., sprinting followed by walking). Benefits: Improves cardiovascular health Aids in weight loss Enhances endurance Considerations: May be repetitive Potential for overuse injuries 4. Yoga and Pilates Yoga and Pilates focus on flexibility, core strength, and balance. Yoga incorporates breathwork and mindfulness, while Pilates emphasizes controlled movements and core stability. Both are excellent for improving overall flexibility and strength. Benefits: Enhances flexibility and core strength Reduces stress Improves posture Considerations: May not be sufficient for those seeking intense cardio or strength gains Progress can be slow 5. Functional Training Functional training emphasizes exercises that mimic everyday movements, improving your ability to perform daily tasks. It often includes compound movements that engage multiple muscle groups and improve overall coordination. Benefits: Improves functional strength Enhances coordination and balance Reduces risk of injury in daily activities Considerations: May require specialized equipment Progress can be gradual
Conclusion
The best workout routine is one that aligns with your personal fitness goals, preferences, and lifestyle. Whether you prefer the intensity of HIIT, the muscle-building focus of strength training, or the flexibility benefits of yoga, the key is consistency and gradual progression. By understanding your goals, exploring various workout types, and designing a routine that suits your needs, you can create a fitness plan that not only helps you achieve your objectives but also keeps you motivated and engaged. Remember, the most effective workout routine is one that you can stick to and enjoy, leading to long-term health and fitness success.














Comments
Leave a comment